Block
Block is the foundation of everything.
Block is the most basic unit of execution. It is essentially a piece of code that OOMOL Studio encapsulates in the form of Blocks, making it convenient for users to organize and reuse arbitrarily.
Blocks themselves implement part of the overall business functionality. Users can organize the arrangement order of Blocks and adjust Block code to compose a Flow to achieve business purposes.
If the functionality implemented by a Block is simple and atomic enough, it can be used without restriction in any Flow, thus achieving the purpose of code reuse.
Block itself is a concept independent of Flows. It can be developed and published independently without having to coexist with Flows. When a Block is placed in a Flow, it becomes a Node of the Flow.
Handle
Blocks can accept input parameters and produce output parameters after code execution. Since Blocks are essentially code, neither input nor output is necessary.
Input and output Handles are equivalent to the input and output parameters when defining code methods.
Input Handle
Input Handles can be set or read data from other output Handles, which is passed to the Block code for execution. Input Handles can only connect to output Handles.
Output Handle
Output Handles can only obtain execution results from Block code and cannot set data. Output Handles can only connect to input Handles.
Blocks that have neither input nor output are completely isolated from the outside world. They are not affected by the environment nor do they affect the environment, so we consider such Blocks meaningless.
Script Block
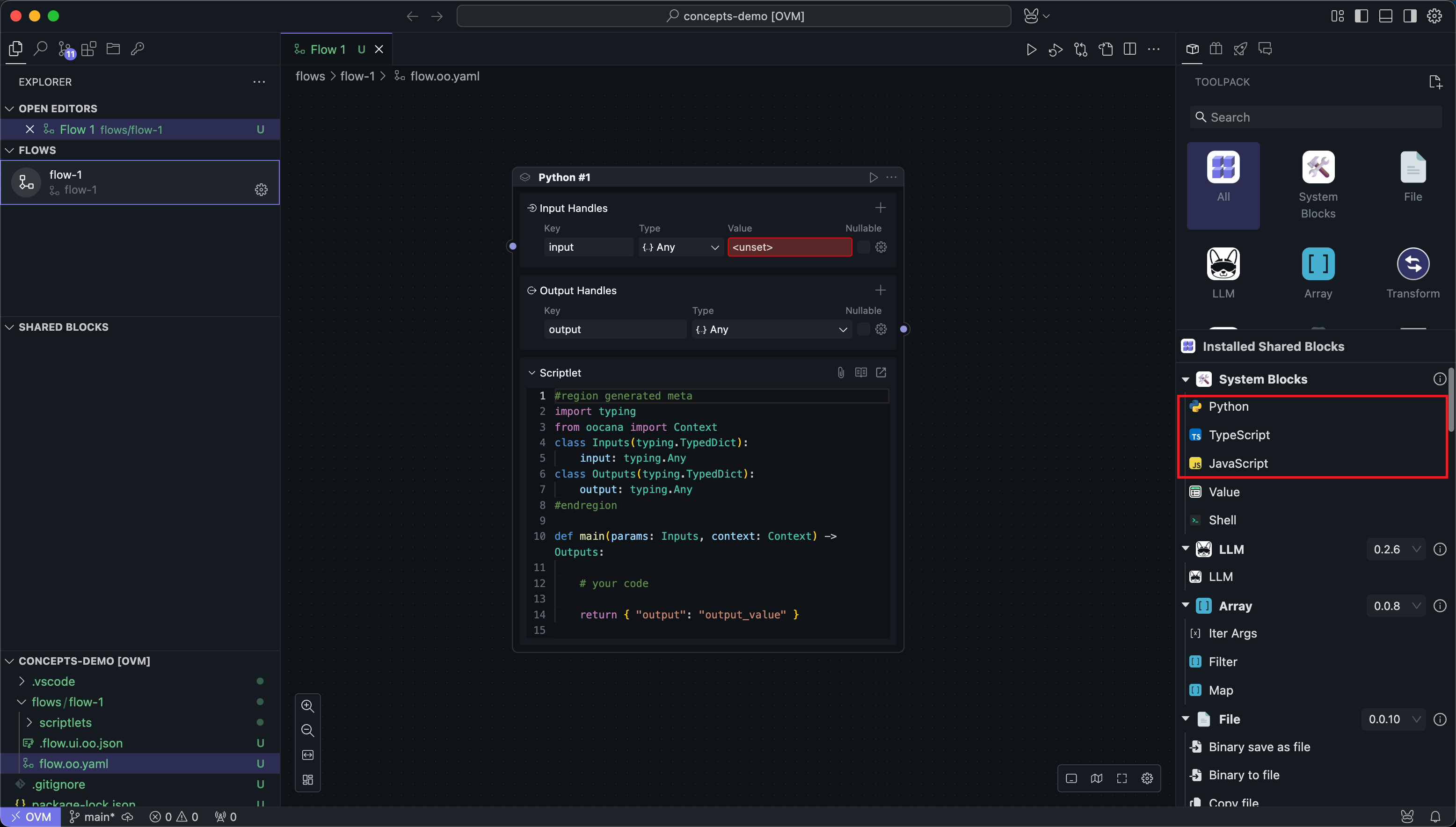

The core of a script Block is the code within it. All running Flows will ultimately execute this code in order to implement functionality through code.
For more information about scripts, please refer to Universal Block Settings and Advanced Script Block Usage.
Shared Block
When you use script Blocks or Flows to implement a reusable function, and you want to use this function in different Flows or share this function with other users, you can convert these Blocks or Flows into a shared Block.
From a usage perspective, compared to script Blocks, shared Blocks only require inputting parameters or connecting wires, except that you don't need to write code.
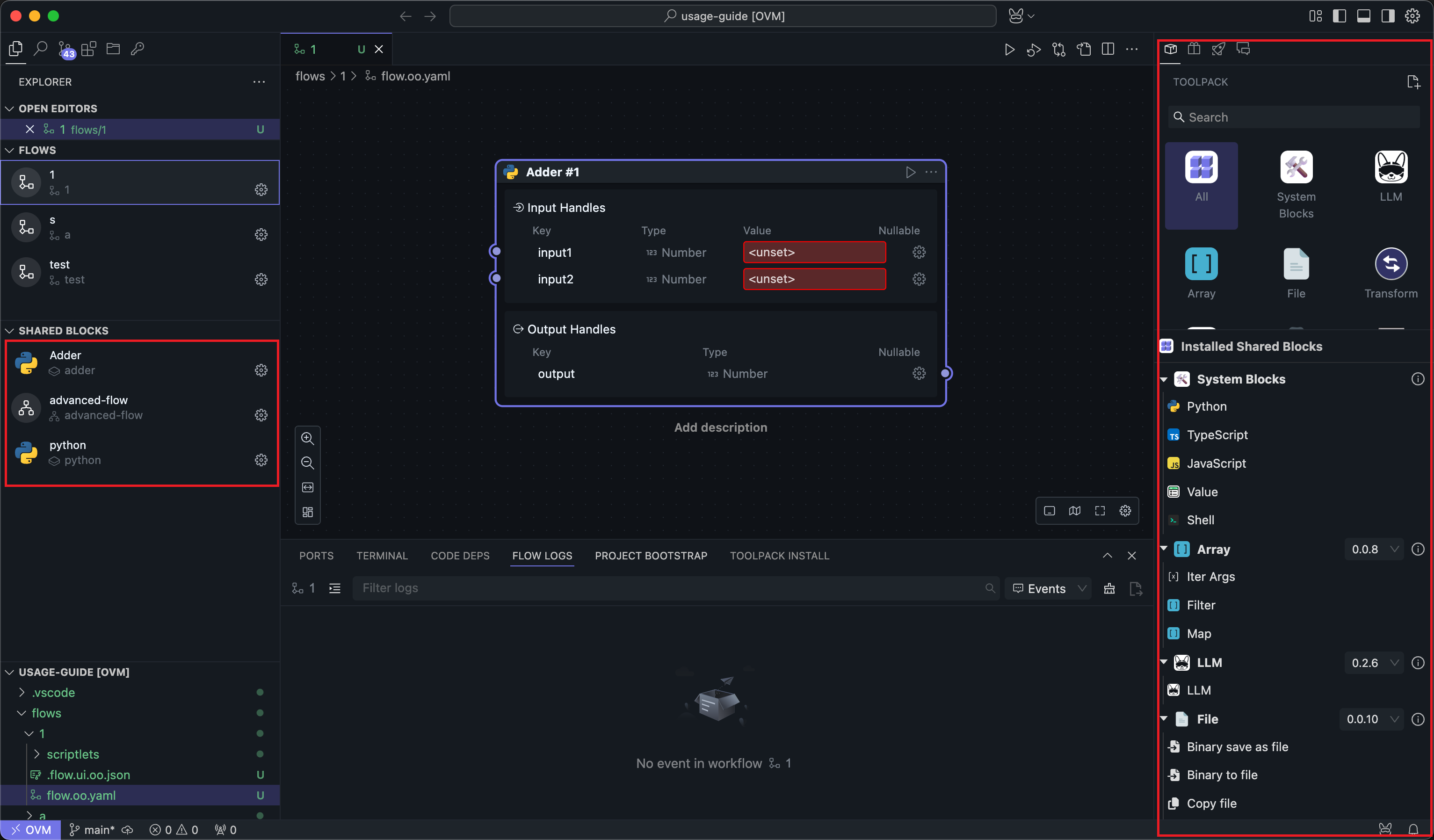

You can find a large number of shared Blocks already created by community users in the right panel, or you can convert script Blocks or Flows into shared Blocks yourself and place them in the left shared Block bar.
Task Block
You can convert a script Block into a shared task Block. Task Blocks fix the code (or functionality) and input/output format of script Blocks, so users only need to fill in parameters and run to get output.
For more information about task Blocks, please refer to Universal Block Settings and Advanced Task Block Usage.
Subflow Block
When you use multiple Blocks to implement a relatively complex function, you can also convert a Flow into a subflow Block, just like converting a script Block into a task Block.
This fixes the content and input/output of the Flow, making it convenient to use in different other Flows or share with other users.
For more information about subflow Blocks, please refer to Universal Block Settings and Advanced Subflow Block Usage.